Variables
Variables are properties that hold a value or reference to an Object in your game.
These properties can be accessible internally to the Orchestration that contains them, or can accessible externally so that their values can be modified by designers working with instances of the orchestration attached on scene nodes.
Variable Types
Variables can be created using a variety of different types, including data types such as Boolean, Integer, or Float, but can also reference types for holding more complex values like Objects, Nodes, Resources, or other named types. Arrays, Dictionaries, and specialized Packed-Arrays can be created too. Each type is specifically color coded for easy identification:
| Variable Type | Color | Icon | Represents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boolean | #8ca6f0 | True or false value (bool). | |
| Integer | #96c7f0 | Signed 64-bit value between -2^63 and 2^63-1. | |
| Float | #61d9f5 | Signed 64-bit double-precision floating-point number. | |
| String | #6ba6ed | Group of alphanumeric characters, such as Hello World. | |
| StringName | #6ba6ed | An immutable string that is faster to compare than String. | |
| Rect2 | #f291a6 | 2D axis-aligned bounding box using floating-point coordinates. | |
| Rect2i | #f291a6 | 2D axis-aligned bounding box using integer coordinates. | |
| Vector2 | #bd91f2 | 2D vector using floating-point coordinates. | |
| Vector2i | #bd91f2 | 2D vector using integer coordinates. | |
| Vector3 | #d67ded | 3D vector using floating-point coordinates. | |
| Vector3i | #d67ded | 3D vector using integer coordinates. | |
| Vector4 | #d67df0 | 4D vector using floating-point coordinates. | |
| Vector4i | #d67df0 | 4D vector using integer coordinates. | |
| Transform2D | #c4ed69 | 2x3 matrix representing a 2D transformation. | |
| Transform3D | #f5a86e | 3x4 matrix representing a 3D transformation. | |
| Plane | #f77070 | A plane in Hessian normal form. | |
| Quaternion | #ed69a3 | Represents 3D rotations. | |
| AABB | #ed7891 | 3D axis-aligned bounding box. | |
| Basis | #e3ed69 | 3x3 matrix for representing 3D rotation and scale. | |
| Projection | #4da745 | 4x4 matrix for 3D projective transformations. | |
| Color | #9eff70 | RGBA color. | |
| NodePath | #8294ed | Pre-parsed scene tree path, can be relative or absolute. | |
| RID | #69ed99 | Handle for a Resource's unique identifier. | |
| Object | #78f2e8 | Base class for all classes in the Godot engine. | |
| Dictionary | #78edb0 | Container that holds key-value pairs. | |
| Array | #e0e0e0 | Container that holds a sequence of elements. | |
| Callable | #78f2e8 | Represents a method or a standalone function callback. | |
| PackedByteArray | #8ca6f0 | Packed array of byte values. | |
| PackedStringArray | #6ba6ed | Packed array of String values. | |
| PackedInt32Array | #96c7f0 | Packed array of 32-bit integer values. | |
| PackedInt64Array | #96c7f0 | Packed array of 64-bit integer values. | |
| PackedFloat32Array | #61d9f5 | Packed array of 32-bit floating-point values. | |
| PackedFloat64Array | #61d9f5 | Packed array of 64-bit floating-point values. | |
| PackedVector2Array | #bd91f2 | Packed array of Vector2 values. | |
| PackedVector3Array | #d67ded | Packed array of Vector3 values. | |
| PackedColorArray | #9eff70 | Packed array of Color values. |
We are aware that variables cannot be assigned to all Godot engine values, such as enumerations. We are also aware that exporting of certain variables as flags and enumerations also is not available. There is currently an upcoming fix to introduce a revamped Variable UI to allow defining variables of any Godot type more easily.
Connection colors can be adjusted in the Project > Project Settings > Orchestrator > UI section.
Exported variables
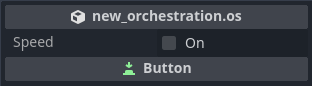
For a variable to be modified from outside the orchestration, it must be exported.
Variables in the component panel are private by default, using the
Once a variable has been exported, if the orchestration is attached to any scene nodes, the value of the variable can be initialized for each specific scene node that the orchestration is attached separately.
This allows for creating orchestrations with unique behaviors and reusing that behavior on different nodes, but allowing each node to work differently based on unique per-node configurable values.
Private variables
By default, a variable is private, or not exported.
Private variables are those that can be modified from within the owning orchestration graphs; however, are not accessible from external actors such as C#, GDScript, or other orchestrations.
You can determine whether a variable is private if it has the
Variable descriptions
While Orchestrator allows you to define a variable description, these descriptions are only for informational purposes. At this time, these descriptions are not exposed in the tooltips for exported variables; however, this is planned for a future patch.
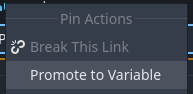
Promoting to variable
Variables can also be created automatically by using the Promote to Variable context-menu option. Right-click any input or output data pin on an orchestration node and select Promote to Variable.
Accessing variables
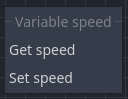
When working with variables in an orchestration, you will access them in one of two ways: by using the Get node (referred to as a Getter or Accessor) to get the value of the variable or by using the Set node (referred to as a Setter or Mutator) to set the value of the variable.
You can create a Set node or a Get node for a variable by right-clicking in the graph and typing either Set (variable name) or Get (variable name). Another method is to drag and drop the variable onto the graph canvas, selecting to spawn either a Set or Get node.
Editing variables
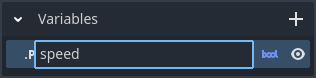
Variable values can be set either as part of the orchestration's node graph or as a default value in the Inspector view. When setting a default value on an exported variable, the default value will be overridden if the scene node that the orchestration is attached specifies a custom value in the Inspector. To set variable default values:
- Click the variable in the component panel.
- In the Inspector view, modify the value associated with the Default Value property.
Not all variable types allow specifying default values.
For example, if the variable represents a Node or a Godot Object type, then the default value property won't be available.
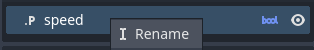
Renaming variables
To rename a variable:
- Right-click the variable in the component panel, and select Rename in the context-menu.
- Enter the new variable name in the text box and press Enter.
Any Get or Set node already in any graph will automatically update when the variable is renamed.
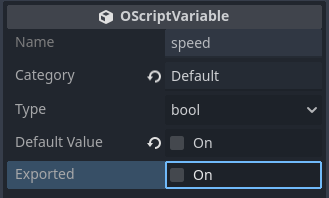
Variable properties
You can set all the properties for a variable in the Inspector panel. Some variables may have more or less properties than others, depending on the variable's type.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the variable, can only be changed from the component panel. |
| Category | The logical group the variable belongs. Setting this to an empty string or Default implies the variable is uncategorized. |
| Type | Specifies the type the variable represents. |
| Exported | Toggles whether the variable is publically accessible outside the Orchestration when checked. |
| Default Value | For many variable types, sets an initial, default value assigned to the variable when the orchestration is created. |
| Description | Specifies a custom description that describes the variable, its purpose, and usage. |
Getting and setting variable values
Variables can also be edited as part of your orchestration graphs by using the Get and Set nodes. The easiest way to create them is by dragging a variable from the component panel onto the graph. A small context-menu will appear asking if you would like to create a Get or Set node.
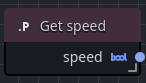
Get nodes
A variable Get node returns the variable's value to in the orchestration. Once created, these nodes can be plugged into any node that takes the appropriate variable type.
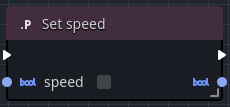
Set nodes
A variable Set node changes the value stored in the variable. Note that these must be called by an execution pin in order for the node to execute and set the variable's value.
Shortcuts when dragging
- Ctrl-drag: Creates a Get node
- Alt-drag: Creates a Set node