Constants
Constants are an integral part of any programming language, as they provide a human-readable names to special values.
For example, in mathematics, there are numerous constants called TAU and PI, and Orchestrator supports these and many more.
In this section, you will learn what are Orchestrator's constant types, and how to use them.
Constant nodes are considered experimental
Class-specific constants
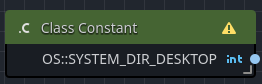
Class-specific constants are constants that must be accessed by using the class as a prefix.
For example, if your game needs to access the SYSTEM_DIR_DESKTOP, you would do so by using the OS class.
In GDScript, the code would look like:
var desktop_directory = OS.SYSTEM_DIR_DESKTOP
To access a class-specific constant in Orchestrator:
- Right-click the graph to open the All Actions dialog.
- Search for
Class constant. - Press the Add button or simply press Enter.
Once the node has spawned, select the node in the Graph and adjust its properties in the Inspector view.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Class Name | The Godot class that owns the constant, i.e. OS. |
| Constant | The constant value to output from the node when executed, i.e. SYSTEM_DIR_DESKTOP. |
Global constants
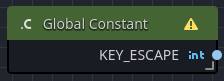
Global constants are very similar to class-specific constants; however, since they are in the global namespace, they do not require the use of a prefix to access.
For example, if your game needs base behavior around the constant for the ESC key, you would use the KEY_ESCAPE global constant.
To access global constants in Orchestrator:
- Right-click the graph to open the All Actions dialog.
- Search for
Global constant - Press the Add button or simply press Enter.
Once the node has spawned, select the node in the Graph and adjust the properties in the Inspector view.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Constant | The constant value to output from the node when executed, i.e. KEY_ESCAPE. |
Math-specific constants
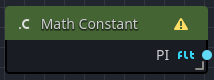
Godot specifically registers math-specific constants slightly differently, therefore in order to access constants such as One, PI, PI/2, TAU, and others, you must use a Math Constant node.
To access math constants in Orchestrator:
- Right-click the graph to open the All Actions dialog.
- Search for
Math constant - Press the Add button or simply press Enter.
Once the node has spawned, select the node in the Graph and adjust the properties in the Inspector view.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Constant | The constant value to output from the node when executed, i.e. PI. |
Singleton-specific constants
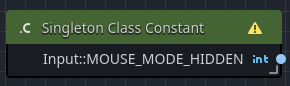
Singleton-specific constants are very similar to class-specific constants; however, these are related specifically to Godot's registered singleton objects, such as Input or AudioServer.
For example, to access MOUSE_MODE_HIDDEN or MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED, you would use a Singleton Constant node.
To access singleton constants in Orchestrator:
- Right-click the graph to open the All Actions dialog.
- Search for
Singleton constant - Press the Add button or simply press Enter.
Once the node has spawned, select the node in the Graph and adjust the properties in the Inspector view.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Class Name | The singleton class to scope the constants based upon, i.e. Input. |
| Constant | The constant value to output from the node when executed, i.e. MOUSE_MODE_HIDDEN. |
Type-specific constants
Type-specific constants are similar to class-specific constants; however, these are related specifically to Godot built-in data types.
For example, if you want to use Vector3.ZERO to set a Vector3 to its default value, you would use a Type Constant node.
To access type constants in Orchestrator:
- Right-click the graph to open the All Actions dialog.
- Search for
Type constant - Press the Add button or simply press Enter.
Once the node has spawned, select the node in the Graph and adjust the properties in the Inspector view.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic Type | The Godot built-in type to scope the constants based upon, i.e. Vector3. |
| Constant | The constant value to output from the node when executed, i.e. ZERO. |