Math
Math nodes are essential to every game, allowing a script to do anything from moving an object each frame to computing the probability of specific scenarios based on a wide array of input chracteristics. Godot, and by extension Orchestrator, provide dozens of mathematical nodes to perform any type of computation.
Operators
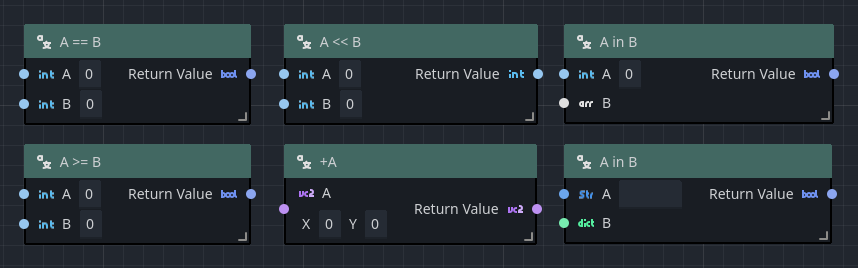
Orchestrator classifies math operations into 5 key groups:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Boolean | Compares two values to determine their equality or relative coparison. Examples: ==, !=, <, <=, >, or >= |
| Numeric Math | Performs a unary operation on a single value or binary operation on two or more values. Examples: +, -, *, /, -Unary, +Unary, %, or ^ (power). |
| Bitwise | Performs bitwise operations on a given numeric value. Examples: Shift left, Shift right, And, Or, Xor, or Negate. |
| Logic | Performs a logical comparison between one or two values. Examples: And, Or, Xor, and Not |
| Containment | Checks whether a value is contained within a collection. Examples: has or contains |
Orchestrator looks at all the possible combinations of operations between various data types and generates a unique operator node for each combination.
For example, the node to add two Integer values differs from a node that adds two Float values.
At first glance, this may seem strange, but it's generally better in visual scripting to enforce a bit more type safety than in text-based code where it's much easier to point the user to a specific line when a type coercion or invalid value is recognized. The following shows several different examples of various math operator nodes.
Add math nodes
To add a math node to the orchestration, simply:
- Right-click the graph to access the All Actions dialog.
- Search for the math operation, for example
Multiply. - Select the right math operation for the two operand types.
Math nodes are initially categorized by the first operand type.
For example, the Multiply node that accepts an Integer as the first argument will be under the Math > Integer category.
The operand type included in the parenthesis that follows the operation specifies the second argument type.
So to add a node that multiplies an Integer with a Float, you would search for the Multiply node under the Math > Integer category, selecting the action labeled Multiply (Float).
Changing math operands
After placing a Math node, if you need to change the operand type of one of the input values, then you must select a new node that matches your desired operands. By following the Add math nodes procedure, you can add the appropriate node and connect all the input/output pins before removing the old node.
To remove the old node, simply:
- Select the node in the graph.
- Either Right-Click and select Delete from the context-menu or simply press the
Delbutton.