Flow Control
Flow Control nodes are some of the most common types of nodes used in visual scripting, as they provide the control over the sequence of how an Orchestration's nodes are executed.
Switch nodes
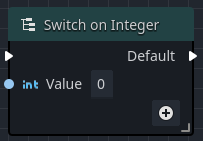
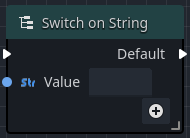
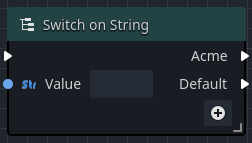
A switch node reads a data input, and based on that value, sends the execution flow out to the matching (or optional default) execution output pin. There are several types of switches available: Integer, String, and Enumeration.
In general, switches have an execution input, and a data input for the type of data they evaluate. The outputs are all execution outputs. Enumeration switches automatically generate the output execution pins based on the enumeration's properties, while Integer and String switches provide customizable output execution pins.
Editing switch nodes
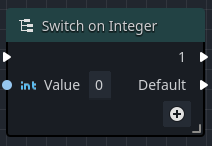
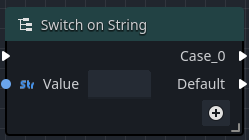
When an Integer or String switch node is added to an Orchestration, the only output execution pin that is available is the Default pin.
The Default output execution pin will fire if the input fails to match any of the other specified output pins, or if no other output pins are defined.
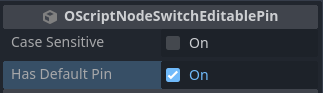
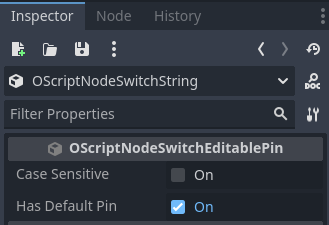
It can be removed by unchecking the Has Default Pin property in the Inspector view.
Editing an Integer switch
- Select the switch node in the Graph to display its properties in the Inspector view.
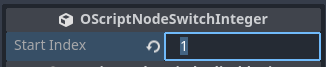
- Change the Start Index to the lowest integer value that you want to check against.
- Click on the button to add a new output pin with the Start Index value.
Clicking on the
Removing an output execution pin on a Switch on Integer node causes any higher-valued pins to decrease their value by 1.
Editing a String switch
- Select the switch node in the Graph to display its properties in the Inspector view.
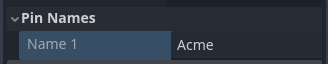
- Click on the button on the node in the Graph to add new output pins.
- A new expandable section called Pin Names will appear in the Inspector view.
- Adjust the names of all the output pins accordingly.
Repeat the process for any additional output pins you would like to add. To remove an output execution pin, right-click on the pin name and select Remove Pin.
Standard flow control nodes
These nodes provide a variety of means to control the execution flow of an orchestration.
Branch
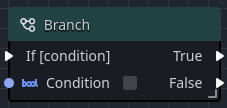
The Branch node serves as a simple way to create decision-based flow from a single true/false condition. Once executed, the Branch node looks at the incoming value of the attached boolean input, and outputs an execution pulse down the appopriate output.
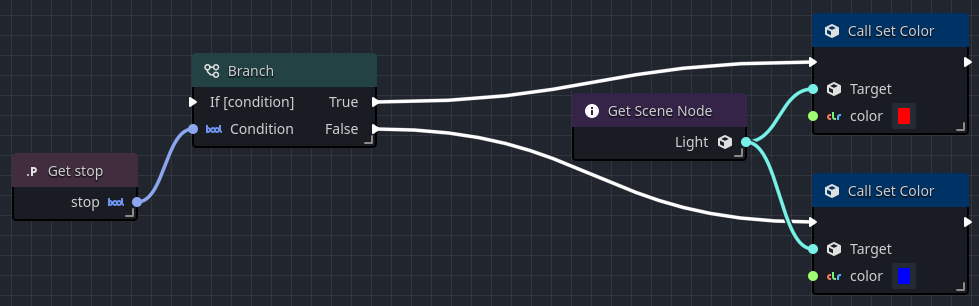
In this simple example, the branch is checking the current state of a boolean variable.
If true, it sets the color of a light to be red.
If false, it sets the color to blue.
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Condition | Takes a boolean value used to indicate which output pin that will be triggered. |
| True | This outputs an execution pulse if the incoming condition was true. |
| False | This outputs an execution pulse if the incoming condition was false. |
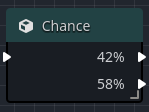
Chance
The Chance node works by calculating a value between 0 and 100, and sending the execution out one of two output pins.
The percentage chance is set in the Inspector view by setting the value of Chance to a value between 0 and 100.
- If the random value generated is between 0 and the specified
Chance, the top output pin will be chosen. - If the random value generated is greater than the
Chancevalue and less-than equal to 100, the bottom output pin will be chosen.
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Top Output Pin | The output pin that emits a pulse if the random value is between 0 and Chance (chance inclusive). |
| Bottom Output Pin | The output pin that emits a pulse if the random value is between Chance and 100 (chance exclusive). |
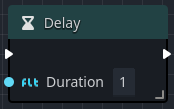
Delay
A Delay node works by temporarily yielding the execution of the orchestration without blocking the game loop.
The is done by using coroutines and Godot signals to await on the internal timer's timeout callback.
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Duration | Specifies the number of seconds to yield the orchestration by, defaults to 1 second. |
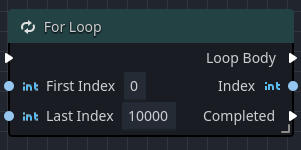
For loop
The For Loop node works like a standard code loop, firing off an execution pulse for each index between a start and end value.
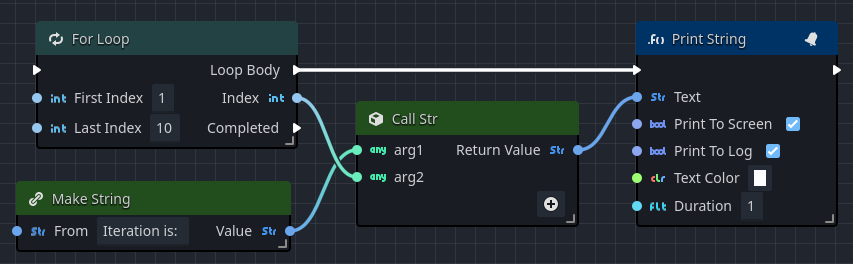
In the following simple example, the loop is triggered when the player touches a simple level trigger. The loop iterates 10 times, each time calling a Print String, logging a prefix message with the current iteration.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| First Index | Takes an integer representing the first index in the loop (inclusive). |
| Last Index | Takes an integer representing the last index in the loop (inclusive) |
| Loop Body | This outputs an execution pulse on each iteration of the loop as it moves between the two indices. |
| Index | This outputs the current index in the loop. |
| Completed | This outputs an execution pulse when the loop has reached the for loop has completed. |
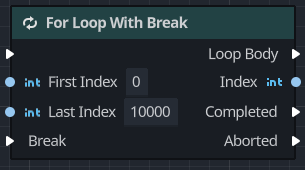
For loop with break
The For Loop With Break node works in a very similar manner to the For Loop node, except that it includes an input pin that allows for the loop's execution to terminate early.
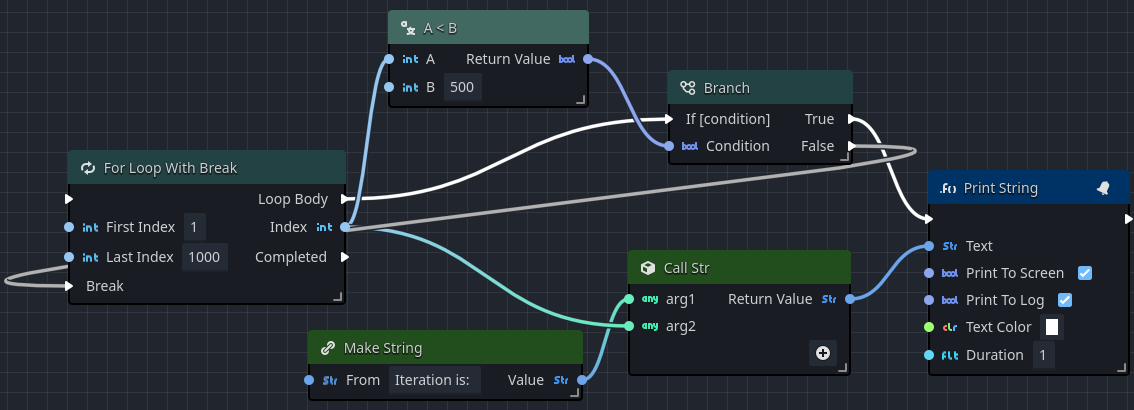
In this simple example, the loop is triggered when the player touches a simple level trigger. The loop iterates 1000 times, each time hitting a Branch which checks if the loop has hit 500 iterations. If it has not, then a message with the current iteration is placed on the screen. Once it exceeds 500, the Branch sends a pulse into the Break pin, which breaks the loop.
In a future Orchestrator update, wires will be controlled by user-driven Knots, which can be used to render the wire connecting False to the Break input so that they do not automatically pass behind other objects in the graph.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| First Index | Takes an integer representing the first index in the loop (inclusive). |
| Last Index | Takes an integer representing the last index in the loop (inclusive) |
| Break | This execution input pin breaks the loop when triggered. |
| Loop Body | This outputs an execution pulse on each iteration of the loop as it moves between the two indices. |
| Index | This outputs the current index in the loop. |
| Completed | This outputs an execution pulse when the loop has reached the for loop has completed. |
| Aborted | This outputs whether the loop broke early due to the Break input pin. |
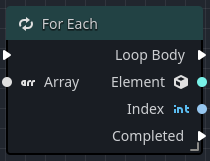
For each loop
The For Each Loop node works in a very similar manner ot the For Loop node, except that this node specifically iterates over a collection.
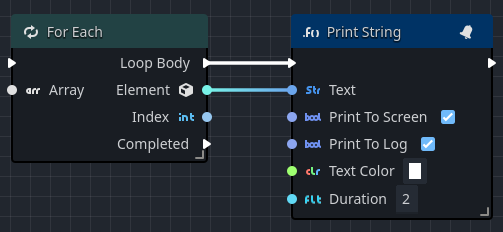
In the above example, the loop is triggered when a player touches a simple level trigger. The loop iterates over a collection, output each element to the screen. Once all elements in the collection have been iterated, the loop exits through the Completed output pin.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Array | The collection to be iterated. |
| Loop Body | This outputs an execution pulse on each iteration of the loop as it moves between the two indices. |
| Element | This outputs the current array element. |
| Index | This outputs the current index in the loop. |
| Completed | This outputs an execution pulse when the loop has reached the for loop has completed. |
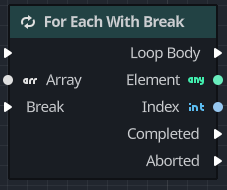
For each loop with break
The For Each Loop With Break node works in a very similar manner to the For Each Loop node, except that it includes an input pin that allows for the loop's execution to terminate early.
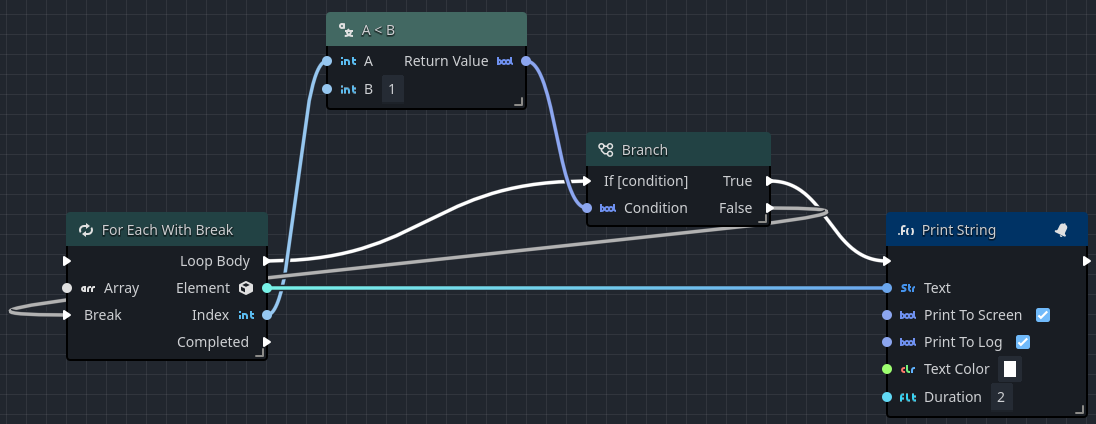
In this simple example, the loop is triggered when the player touches a simple level trigger. The loop iterates for each element in the array, each time hitting a Branch which checks if the loop has hit the second element. If it has not, then a message with the current element is placed on the screen. Once the second element is reached, the Branch sends a pulse into the Break pin, which breaks the loop.
In a future Orchestrator update, wires will be controlled by user-driven Knots, which can be used to render the wire connecting False to the Break input so that they do not automatically pass behind other objects in the graph.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Array | The collection to be iterated. |
| Break | This execution input pin breaks the loop when triggered. |
| Loop Body | This outputs an execution pulse on each iteration of the loop as it moves between the two indices. |
| Element | This outputs the current array element. |
| Index | This outputs the current index in the loop. |
| Completed | This outputs an execution pulse when the loop has reached the for loop has completed. |
| Aborted | This outputs whether the loop broke early due to the Break input pin. |
Random
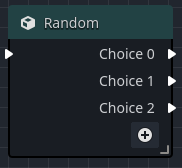
A Random node allows specifying one or more output execution pins, and one will be chosen randomly when the node executes.
To add a new output execution, simply click the
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Choice_n | A random choice output execution between 0..n depending on the number of random choices added. |
Select
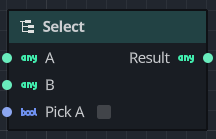
A Select node acts like a gate, emitting one of two different input values referred to as A and B based on a condition.
If the condition is true, the Select node allows the value of A to be sent as the output value.
If the condition is false, the Select node allows the value of B to be sent as the output value.
By default, the Select node uses the Godot Any type to allow any value to be attached to its input pins.
To restrict the Select node to a specific Godot type, right-click on the A, B, or Result pins and pick a type from the Change Type context-menu.
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| A | One of two values that will be output if the Pick A condition is true. |
| B | One of two values that will be output if the Pick A condition is false. |
| Pick A | Controls whether the value of A or B is emitted as the Return Value |
| Result | The output value of the gate, depends on what the Pick A condition is. |
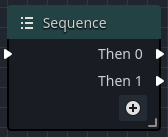
Sequence
A Sequence node allows the execution of two or more execution chains in sequential order, by first executing the connections of Then 0, followed by Then 1, and so on until all output connections have been called.
Additionally, new output connections can be added by pressing the
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Then 0 | The first output connection chain to be executed, and cannot be removed. |
| Then 1 | The second output connection chain to be executed, and cannot be removed. |
| Then n | The next output connection chain to be executed, any chain where n >= 2 can be removed. |
Type cast
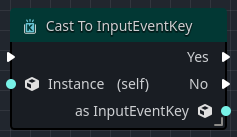
A Type Cast node is a special type of flow control type that allows for checking the input value's logical type.
When the input value's type matches the configured type in the node, the Yes output pin will receive the output pulse, and the as ... output data pin will contain the value cast to the desired type.
When the input value's type does not match the configured type in the node, the No output pin will receive the output pulse, and the as ... output data pin will be null.
To change the type in the cast operation:
- Select the Type Cast node in the graph.
- In the Inspector view, press the button in the
Typeproperty. - Select the desired type from the dialog.
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Instance | The input value to be checked against the configured Type property. |
| Yes | The output pin that receives the execution pulse if the Instance is a Type. |
| No | The output pin that receives the execution pulse if the Instance is not a Type. |
| as ... | The output data pin that will contain the casted instance as Type, if the cast outputs Yes. |
While
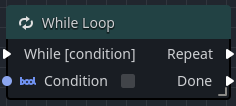
The While node provides a construct similar to a For Loop except the iteration of the loop is driven by an input boolean condition.
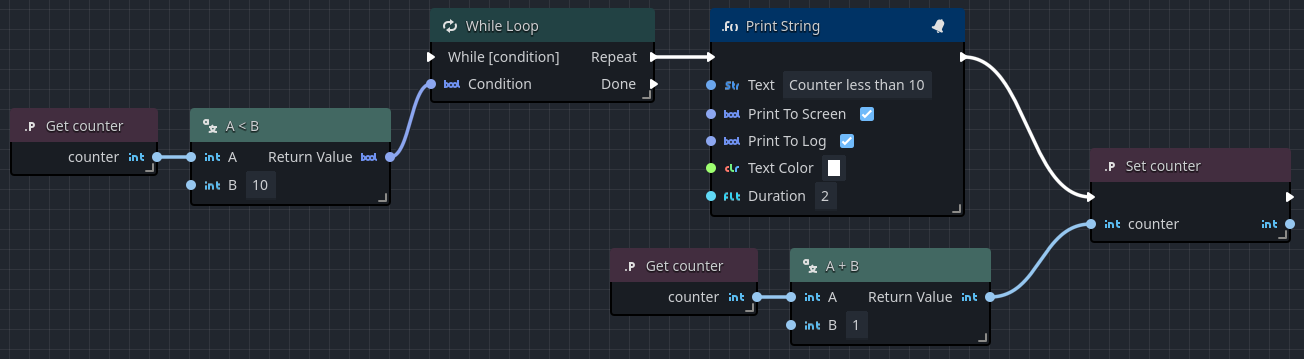
In the following example, we have an integer variable x that is initialized as 0.
The while loop has a boolean condition that checks if x is less-than 10, and if so, will output an execution pulse to the Repeat pin, printing some text onto the screen and incrementing x by one.
When x finally reaches 10, the boolean condition is no longer true, and the while loop ends by emitting an output execution pulse to the Done pin.
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Condition | The condition that is evaluated on each loop iteration. |
| Repeat | The output pin that receives the execution pulse if the condition remains true. |
| Done | The output pin that receives the execution pulse if the condition is false. |