Events
Events are nodes that are called directly by the Godot game engine, to begin the execution of logic within a Graph. They enable orchestrations to perform a series of actions in response to well-defined callbacks within the Godot game engine, such as when the node is ready, enters the tree, receives input, and more.
Events are used to implement new functionality or to override or alter the default functionality of Godot objects. Any number of Events can be used within a single Graph, although you can only define one event node of each event type.
An event can only execute a single, linear series of execution steps. If you want to trigger multiple actions from one event, you will need to string them linearly together.
To add an event to the Graph:
- Press the button in the Functions section of the Components view.
- Search for the desired Godot event to override in the search box, i.e.
ready. - Press the Add button or simply press Enter.
Once the function override has been added, connect your behavior or add behavior to the output pins of the event node.
Init event
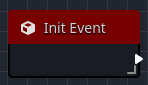
The Init Event is called when the object's script is instantiated, often times after the object has been initialized in memory. This method is very similar to a constructor in most programming languages.
This is useful when you need to perform some initialization steps when the Orchestration is first created.
Orchestrator does not currently support arguments in the init() event callback.
Notification event
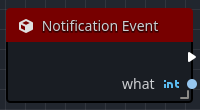
The Notification Event is called when the owning node, and by extension the Orchestration, receives a specific notification from Godot.
Notifications are identified by a what numeric constant, such as NOTIFICATION_PREDELETE.
Normally an Orchestration will prefer to use one of the other overridable events rather than using the Notification Event.
Enter tree event
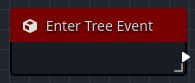
The Enter Tree Event is called when the Orchestration's owning node is added as a child to a node in the scene tree. You will use this event to define behavior that should happen everytime the owning node enters the scene.
Exit tree event
The Exit Tree Event is called when the Orchestration's owning node is removed from the scene tree. You will use this event to define behavior that should happen everytime the owning node leaves the scene, such as clean-up specific resources that may have been allocated during the script's lifetime.
Input event
The Input Event is called when the Orchestration's owning node receives some type of input.
The output pin event will provide the orchestration with the input event that was received by the engine.
Physics process event
The Physics Process Event is called during the physics processing in during the main game loop.
This event is synchronized with the physics frame rate, i.e. the delta value should always be constant and in seconds.
This event callback is great to perform logic that should be synchronized with physics.
If the owning node does not have physics enabled, the Physics Process Event will not be called. Additionally, if the owning node has been removed from the scene, this event will not be called.
Process event
The Process Event is called during the processing step of the main game loop.
This event is fired every frame and as fast as possible, meaning that delta will not be consistent and can vary.
The delta represents the time since the previous frame, and is represented in seconds.
This event callback is great to perform per-frame (per tick) logic.
If the owning node does not have processing enabled, the Process Event will not be called. Additionally, if the owning node has been removed from the scene, this event will not be called.
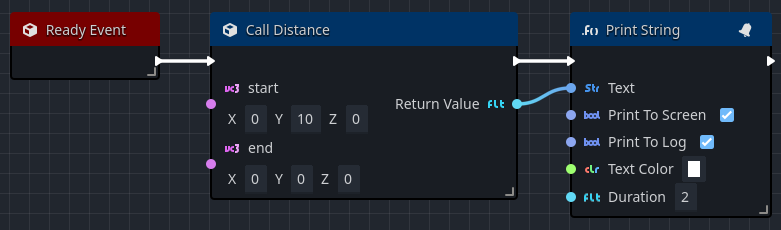
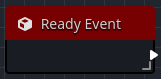
Ready event
The Ready Event is called when the owning node, and by extension the Orchestration, is "ready". Godot implies readiness when the owning node, and any children, have all entered the scene and their respective Enter Tree Event callbacks have executed.
This event callback is typically used for initialization, especially if the behavior expects the Orchestration to exist in the scene.
Godot executes the Ready Event of child nodes before parent nodes.
This callback is only fired once for each Orchestration.
If the Orchestration's owning node is removed from the scene and later added, the Ready Event is not called a subsequent time.
If the Orchestration's Ready Event should be called again when added back to the scene, a prior call to the Orchestration's request_ready() function must be made.
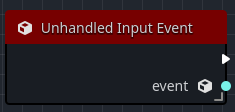
Unhandled input event
The Unhandled Input Event is called when an InputEvent has not been consumed by any _input or UI Control objects.
It is called after the Unhandled Key Input Event, and is called in a bottom up order through the scene tree.
The output pin event contains the received InputEvent object.
This callback is an excellent place to handle non-key related input, such as mouse interactions.
If the owning node has disabled processing of unhandled input via set_process_unhandled_input with false, this method is not called.
Additionally, if the owning node has been removed from the scene, this event will not be called.
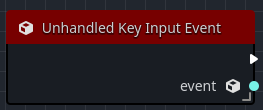
Unhandled key input event
The Unhandled Key Event is called when an InputKeyEvent has not been consumed by any _input or UI Control objects.
It is called before the Unhandled Input Event, and is called in a bottom up order through the scene tree.
The output pin event contains the received InputKeyEvent object.
This callback is an excellent place to handle key-related input, such as key pressed or releases.
If the owning node has disabled processing of unhandled input via set_process_unhandled_key_input with false, this method is not called.
Additionally, if the owning node has been removed from the scene, this event will not be called.
Custom Events
Other game engines provide the ability add user-defined custom events. In Godot, these are known as Signals. Please see the Signals section for details on how to add and work with signals using Orchestrator.