Dictionary
One of Godot's built-in types is a Dictionary, which is responsible for storing key-value pairs.
Dictionaries are associative containers that preserve insertion order.
In other languages, these are often referred to a hash map or an associative array.
The Orchestrator documentation does not get into the specifics of what a Dictionary is or is used for at a fundamental level.
If you need more details on what a Dictionary is or what you may need or want to use such a type, please see the Godot documentation.
Overview
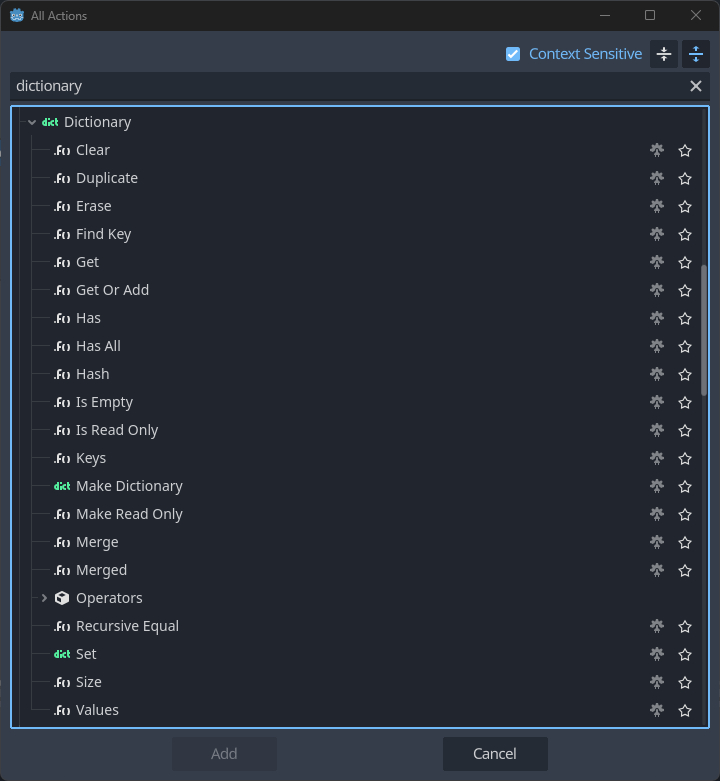
The Godot engine exposes a variety of nodes to operate on Dictionary container types, such as getting an entry by key, removing an entry by key, or getting the size of the dictionary to name a few.
These operations can all be found by searching for dictionary in the All Actions search window, some shown below:
Orchestrator extends the Godot Engine by introducing two custom node types, denoted by the special
For any Godot provided Dictionary action, you can view the documentation for that action in the Godot Editor by right-clicking the node in the graph and clicking the
Creating a dictionary
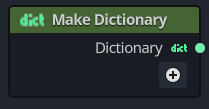
To create a new Dictionary to store key/value pairs, select the Make Dictionary action in the All Actions search window.
The node is designed to accept zero or more key/value pairs.
When the node is first placed onto the graph canvas, it will return an empty Dictionary, as illustrated here:
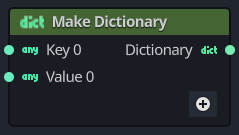
To add key/value pairs to the Dictionary during construction, press the
The
Node properties
The following describes the input and output pins for the Make Dictionary node.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
This is the entry's key value that will be used to uniquely identify the value in the Dictionary. | |
This is the entry's value, that will be associated with its match Key n in the Dictionary. | |
The output Dictionary that will contain any defined Value n values associated by the Key n |
When using the Make Dictionary node, each Key n should be unique.
If multiple input key/value pairs use the same Key, only the last pair with the highest index n for Key n will remain.
Setting value in an existing dictionary
In languages like GDScript or C#, the designer uses subscript operators to assign values into a Dictionary.
These operators use the key to effectively insert or displace any existing entry with that key in an already existing dictionary.
Here's a trivial example:
the_dict[the_key] = the_value
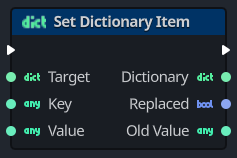
In visual scripting, there isn't a concept of subscript operators, so this operation must be performed using a custom node type that handles the intrinsic subscript manipulation for you. This is precisely what the Set Dictionary Item node does.
This node is extremely powerful as it provides a variety of functionality and information about the operation as outputs. See the node properties section for details on the input and output pins.
Node properties
The following describes the input and output pins for the Set Dictionary Item node.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
This is the target Dictionary that will be modified by this node. | |
| This is the dictionary key (a wildcard) to be inserted or modified by this node. | |
| This is the value (a wildcard) associated with the key that will be added by this node. | |
This is the modified Dictionary, after the key has been added by the node. | |
This represents whether an existing entry with the Key was replaced if the value is true. | |
This is the old value (a wildcard) that was replaced for the Key, if the Replaced output pin is true. |